- 1. Enhanced Collaboration BIM allows all project stakeholders to work together in real-time on the same digital platform. This ensures better communication, fewer mistakes, and faster approvals.
- 2. Early Problem Detection BIM can detect clashes—like overlapping pipes or ducts—before construction starts. Identifying issues early prevents costly rework later on.
- 3. Accurate Budgeting and Scheduling BIM supports 4D (time) and 5D (cost) modeling. This means project managers can better estimate timelines and budgets, making the entire process more predictable and efficient.
- 4. Realistic Visualization Clients and teams can view the finished building virtually before it’s even built. This helps with decision making, design changes, and client satisfaction.
- 5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency With energy analysis tools built into BIM software, designers can create eco-friendly buildings that save resources and reduce environmental impact.
- 6. Simplified Maintenance After construction, the BIM model acts as a digital manual—storing essential data about systems, components, and maintenance schedules for easier facility management.
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced construction world, accuracy, collaboration, and innovation are key to building better and faster. This is where BIM modelling, or Building Information Modelling, plays a game changing role. But exactly what is BIM modelling, and why has it become so essential in the fields of architecture, engineering, and construction?
In this article, we’ll explore BIM in a friendly, easy-to-understand way—breaking down what it is, how BIM scanning, its major benefits, real-world uses, and the exciting future that lies ahead.
What Is BIM Modelling?
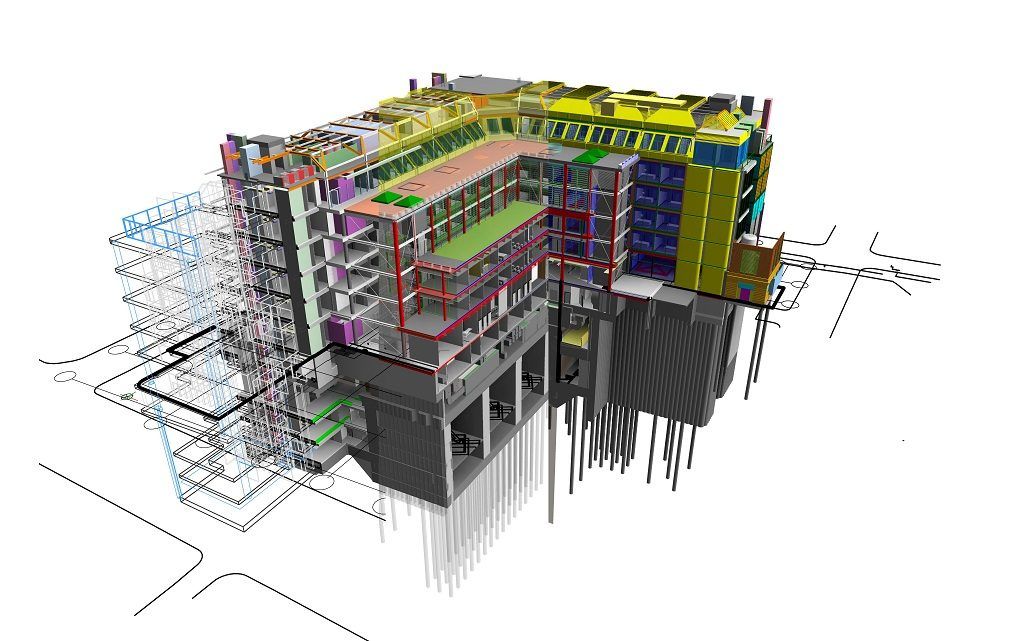
BIM modelling is a digital process used to design, build, and manage buildings and infrastructure. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM creates intelligent 3D models that include detailed information about every component of a structure—materials, dimensions, costs, schedules, energy efficiency, and more.
More than just a visual model, BIM acts as a shared knowledge resource. Architects, engineers, builders, and facility managers all work on the same model, making collaboration smoother and decision-making smarter throughout the project’s lifecycle.
What Is BIM Scanning?
BIM scanning, also known as laser scanning or 3D scanning, is the process of capturing real-world data using advanced scanning technology. It involves using laser devices such as a lidar 3d scanner to scan existing structures and environments, creating precise 3D models filled with accurate measurements.
This technique is especially useful in renovation projects or when working with older buildings without digital plans. BIM scanning improves accuracy, helps detect flaws, and supports better planning from the very beginning.
Key Benefits of BIM Modelling
Now that you know what BIM modelling is, let’s take a look at why it’s such a powerful tool in modern construction and design.
Real-World Uses of BIM Modelling
BIM modelling is used across many sectors and project types, including:
Architecture:
To design functional, aesthetic, and safe structures
Construction:
For efficient planning and execution
Civil Engineering:
To build infrastructure like bridges, tunnels, and roads
Urban Planning:
For creating smarter, more organized cities
Real Estate:
To give clients immersive 3D walkthroughs
Facility Management:
For long-term building operations and upgrades
Future Trends in BIM Modelling
Technology never stands still—and neither does BIM. Let’s look at what the future holds:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is set to automate design workflows, predict risks, and optimize building performance using BIM data.
2. Cloud-Based Collaboration
BIM platforms hosted in the cloud allow seamless access and real-time collaboration between teams located anywhere in the world.
3. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a live, up-to-date virtual replica of a building. Connected with sensors, it provides real time data for monitoring and maintenance.
4. Augmented & Virtual Reality
AR and VR take BIM to a whole new level—allowing users to “walk through” buildings during design or view models on-site for better accuracy.
5. Green Building Support
With climate change concerns growing, BIM will play a key role in designing sustainable buildings with reduced energy use and carbon emissions.
Final Thoughts
So, what is BIM modelling? Simply put, it’s a smart, digital approach to designing, building, and managing structures from start to finish. Combined with the precision of BIM scanning, it provides a detailed and efficient workflow that minimizes errors and maximizes value.
Whether you're an architect, builder, engineer, or property developer, adopting BIM today means preparing your projects for a smarter, greener, and more efficient tomorrow.
Read More: What is BIM Scanning? Benefits, Process & Applications