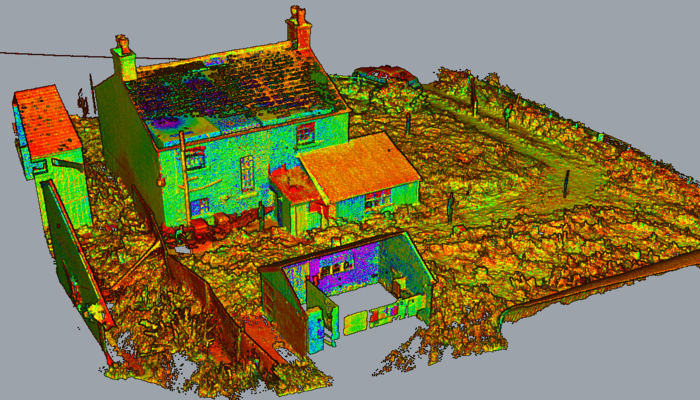
Introduction:
In many fields, including building, urban planning, natural resource conservation, and even archeology, surveying and mapping are common procedures.
With lasers firing hundreds of millions of times per second and measuring the time it takes for light to package after bouncing off a surface, the LiDAR 3D Scanner creates incredibly accurate 3D point clouds.
Advantages of LiDAR 3D Scanners in Surveying and Mapping
1. High Accuracy and Precision
Although they are used for many different applications, LiDAR 3D scanners capture precise measurements within centimeters of data level, making them an invaluable source of information for projects requiring accurate specifications (infrastructure development, floodplain mapping).
It can penetrate vegetation and capture the ground topography, which gives accurate data in dense forests or uneven terrains.
2. Efficiency and Speed
Unlike traditional surveys, which can take days or even weeks to record such data, LiDAR captures a dense scan of large areas in a fraction of that time. For example, aerial LiDAR systems on drones or aircraft can fly and map hundreds of square kilometers in a single day, meaning project timelines are greatly reduced.
3. Versatility across Environments
LiDAR scanners can be used whether the environment is in urban settings, hilly areas, or in the water. Such versatility is beneficial for applications like city planning, environmental monitoring, and coastal mapping.
4. Enhanced Safety
Surveyors can map hazardous cliffs, construction sites, or disaster zones while staying out of harm's way by using drones equipped with LiDAR sensors.
5. Integration with Modern Technologies
LiDAR data can be easily integrated with GIS, BIM, and other digital platforms. It improves data analysis, visualization, and decision-making processes between applications — particularly in large-scale projects.
Applications of LiDAR in Surveying and Mapping
Urban Planning and Smart Cities
LiDAR comes in handy when testing the effects of virtual buildings with the help of very precise 3D models, making it integral to urban planning. They are used in the modeling of infrastructure, traffic systems management, and utilities planning to lead to smart cities.
Environmental Monitoring
In ecology, it is used to track deforestation, map out wildlife habitats, and analyze how the landscape morphology has changed over time. Because of its capacity for canopy height and density measurement, it is useful in the domain of forestry management.
Disaster Management
One application of LiDAR technology is in the prediction and avoidance of natural disasters. For example, it can create maps of flood-prone areas and detect volcanic activity and landslides generated by earthquakes. LiDAR can generate data shortly after a natural disaster, allowing for speed and convenience in subsequent planning of damage recovery.
Transportation Infrastructure
LiDAR 3D scanners are employed to design and maintain roads, railways, and airports. They allow engineers to analyze current infrastructure and design future projects accurately. LiDAR devices are used to navigate autonomous vehicles and detect obstacles.
Archaeology and Heritage Conservation
LiDAR has converted the surveying of archaeological spots with the eventuality to reveal ancient structures hidden hundreds or, at times, thousands of times under heavy vegetation or soil. This has redounded in the uncovering of long- lost metropolises, temples, and geographies, which have given us unique perceptivity into history societies.
Mining and Geology
LiDAR technology finds tremendous usefulness at numerous stages in mining tasks, including mapping quarries, calculating mineral reserves, and tracking topographical variations over time. Geologists use LiDAR data to explore fault lines, erosion patterns, and other geological phenomena.
Types of LiDAR Systems
1. Terrestrial LiDAR
Terrestrial LiDAR, which is set up on tripods or vehicles, is primarily used to scan and will yield high-resolution scans of structures and smaller areas. It is widely used in site surveys, indoor mapping, and infrastructure inspection.
2. Aerial LiDAR
Aerial LiDAR is typically deployed using drones, helicopters, or airplanes and covers large areas quickly. This becomes useful in applications like topographic mapping, forest canopy analysis, and urban planning.
3. Mobile LiDAR
Mobile systems are vehicle-based, collecting exposure data while in transit. This methodology is useful when tracking direct architectures similar as roads, railroads, etc.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Although LiDAR 3D scanners have revolutionized surveying and mapping, this system faces some challenges. The cost of equipment and the need for trained operators can be limiting factors for adoption. Furthermore, powerful software and computational power are required to process the considerable amount of data produced by LiDAR.
Yet, LiDAR technology has a brighter future ahead. Continued reductions in size and price, paired with advances in AI-driven data analysis, are democratizing LiDAR. Novel applications ranging from LiDAR integration with AR and VR stand to disrupt industries even more.
Conclusion
The revolution in surveying and mapping is a LiDAR 3D scanner. With unmatched precision, speed, and flexibility, they are superseding traditional techniques and opening new horizons across sectors. LiDAR is becoming a Must-Have Tool for Building Our Physical and Digital Worlds As technology progresses, LiDAR is set to become a designated tool for the physical and digital realm.