- Laser Scanner: Emits laser beams and records the time taken for them to reflect back.
- GPS Receiver: Indicates the position of the scanner.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): Measures the scanner orientation.
- Use 3D models of buildings, roads, and public spaces to improve decision-making.
- Evaluate land elevation for flood risk and drainage systems.
- Make a plan for areas that are appropriate for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.
- Oversee construction projects in real-time for safety and environmental compliance.
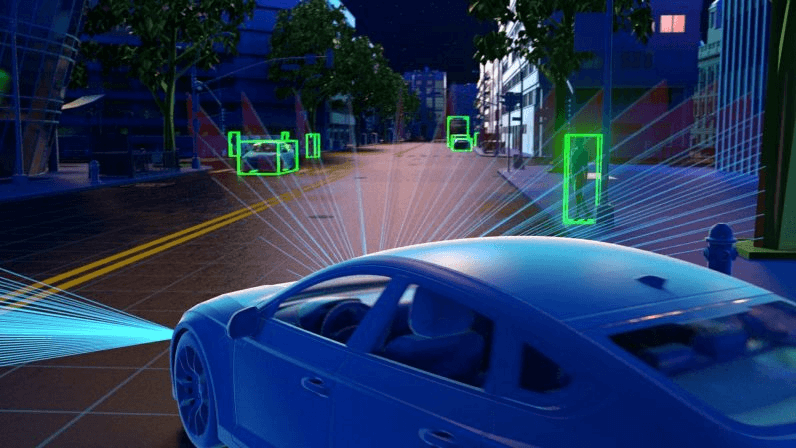
- Improving autonomous vehicle navigation: Autonomous vehicles make use of LiDAR to identify obstacles, pedestrians, and other cars.
- Enhancing traffic flow analysis: Authorities can adjust traffic signals based on real-time congestion data.
- Improving road safety: LiDAR can also detect road defects, potholes, and weaknesses in road bridges and tunnels.
- Planning new roads and public transit routes: LiDAR aids in mapping out topography and assessing existing infrastructure before any new construction takes place.
- Environment Pollution Monitoring: Detecting Air Pollution using LiDAR Sensors.
- Maps of vegetation and green space: Identifies locations for afforestation and the development of urban greens.
- Flood and disaster risk assessment: Assists in mapping flood-prone regions and developing efficient drainage systems.
- Coastal and river monitoring: Monitors change along shores, especially erosion, and water levels.
- Crime prevention: LiDAR data is used by law enforcement agencies to identify areas with high crime rates and to plan effective patrolling routes.
- Plan for Emergency Response: Used to design evacuations and emergency shelters.
- Predicting earthquakes and landslides: LiDAR finds changes in ground and unstable areas.
- Search and rescue: Delivers accurate terrain maps for fires and emergency responders.
- Develop accurate 3D building models for energy and structural monitoring.
- Bridge, Tunnel, and Pipeline Maintenance Prevention
- Analyze the design of urban heat islands and shading effects for optimizing its lighting and energy usage.
- Costly Initial Deployment: LiDAR systems (notably airborne) can prove to be quite expensive.
- Data Processing Complexity: Massive datasets need to be queried and analysed, which does take a lot of processing power. Here you can get all the answers regarding why LiDAR is vital for smart cities.
- Privacy Concerns: Continuous monitoring may lead to the risk of data leaks and privacy invasion.
- Regulatory Issues: There are restrictions on the use of LiDAR in some countries, particularly surveillance in urban areas.
- AI-Driven LiDAR Systems: The future of LiDAR systems will include AI features for real-time decisions.
- Low-Cost and Miniaturized Sensors: 3D mapping for Smart Cities will make it cheaper and more convenient.
- Cloud Storage of LiDAR Data: Cloud computing will revolutionize data storage, sharing, and processing.
- Increased IoT Integration: LiDAR will collaborate with IoT sensors to build a more connected urban environment.
Introduction:
Smart cities are primarily about technology that can enhance urban living, make things more efficient, and create sustainable environments. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) imaging is one of the most transformative technologies in this area. In this blog, we highlight why LiDAR is vital for smart cities, its benefits, use cases, and future prospects.
Understanding LiDAR Imaging
LiDAR offers high-resolution, three-dimensional (3D) spatial data that can be used for urban planning, transportation systems, infrastructure monitoring, environmental analysis, and public safety.
LiDAR systems can be installed on drones, satellites, aircraft, or vehicles to gather real-time data on urban landscapes.
Role of LiDAR in Smart City Development
1) Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Urban planning, space allocation, and overall smart city management need granular spatial information. Benefits to city planners provided by LiDAR imaging:
2) Smart Transportation and Traffic Management
Smart cities are characterized by efficient transportation. 3D Mapping for Smart Cities contributes by
3) Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability
laser mapping plays a key role in environmental analysis and sustainability initiatives, for instance:
4) Public Safety and Disaster Management
Smart cities even aim at ensuring public safety. LiDAR imaging aids in:
5) Digital Twin Technology and Smart Buildings
Digital twin technology refers to creating a virtual representation of physical infrastructure or assets to monitor their performance and predict potential issues in real time. LiDAR is used to:
Advantages of LiDAR Imaging in Smart Cities
1. High Accuracy and Precision
With centimeter-level accuracy, LiDAR scanning in smart city projects acquires comprehensive spatial data as opposed to the traditional surveying methods.
2 Fast and Efficient Data Collection
LiDAR, on the other hand, captures massive amounts of data in a matter of hours, enabling swift decision-making as it speeds up the survey process compared to manual surveys.
3 Works in Different Environments
Well-lit or low-light, in cities, forests, or close to the coast, LiDAR works just as well in almost any environment.
4. Supports automated processes and artificial intelligence
Laser mapping can be combined with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to add value in performing analytics, for example, traffic congestion prediction or prediction of structural wear.
5 Cost-Effective in the Long Run
Although the initial cost of a LiDAR system may be the highest in comparison to other sensors, LiDAR minimizes ongoing operational and maintenance costs through higher efficiency and predictive maintenance.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Challenges
Future Prospects
Conclusion
The dynamic and interactive feature of LiDAR imaging is helping to shape smart cities for a vast data approach to urban design. Although there are a few issues, the benefits of the technology outweigh the drawbacks, making it an indispensable tool for the city of tomorrow. Investing in LiDAR scanning in smart city projects allows for planning of smarter municipalities in more resilient, productive, and liveable cities for generations to come. Also Read About Accurate 3D Data Capture